What Is AI Search? Top 3 Things to Know


Large language models (LLMs), like ChatGPT by OpenAI, are being used by people to answer questions and look for information.
Before LLMs, people went to traditional search engines like Google, Bing, or DuckDuckGo and typed in just keywords instead of longer questions to find information.
Business owners and marketers are now being faced with a new challenge: How to get my brand to show up when people go to AI search engines. AI visibility is the new search engine optimization.
Next, I'll introduce what LLMs are, what AI search is, and what you can do today to surface in AI-powered search engines.
I'll give you a hint: You need to master trust-based marketing.
Short summary of the top things to kick things off:
- Search behaviour is changing
- AI searches are hard to influence
- You need a new strategy to optimize for AI search engines.
- If you don't do anything, your competitors will get all the visibility
What Are Large Language Models?
To understand LLMs, you need to understand how they function.
For that, you also need to know what Natural Language Processing (NLP) is.
What Is NLP?
NLP (Natural Language Processing) refers to the traditional approach to teaching computers how to understand and work with text. Before the rise of modern generative AI, NLP relied heavily on human-designed rules, statistics, and probability models.
How Traditional NLP Works
- A human researcher or data scientist manually analyzes text.
- They determine patterns using probability, linguistics, and statistics.
- Based on those insights, they build a model that can do a specific task (classification, sentiment analysis, keyword extraction, etc.).
- The result is a deterministic model, given the same input, it reliably produces the same output.
NLP's Limitations
- Very short context window (often 3–5 words).
- High uncertainty in predictions, shown by high perplexity scores (110+).
- Capable of grammatical output, but not meaningful or coherent long-form content.
- Requires deep manual involvement and domain expertise for every new task.
In other words, traditional NLP involved a lot of human effort for relatively limited results.
What Are LLMs?
LLMs (Large Language Models) represent a newer, deep learning–based approach. Instead of humans crafting rules, the model itself learns language patterns by consuming massive amounts of text.
How LLMs Work
- Billions of parameters (simple functions) are “stitched together” in a deep learning network.
- They learn by observing vast datasets instead of hand-engineered rules.
- The system predicts the next word based on everything that came before it—just at a scale no human could replicate.
- LLMs have enormous context windows, reaching 8,000 words or more.
- They produce responses that are coherent, relevant, and often more polished than those written by humans.
Characteristics of LLMs
- They are stochastic, not deterministic, meaning the same input can yield different outputs.
- They operate as a black box, we don’t fully understand how they arrive at answers.
- They achieve low perplexity scores (around 20), giving them a much tighter “range of good guesses.”
- They can generate text, summarize long documents, reason through sequences, and hold complex conversations.
This is why they sparked such excitement: their output often feels intuitive, contextual, and human-like.
Here's how PhD Kevin Johnson from Dscout visualized the difference between NLP and LLM in 2023:
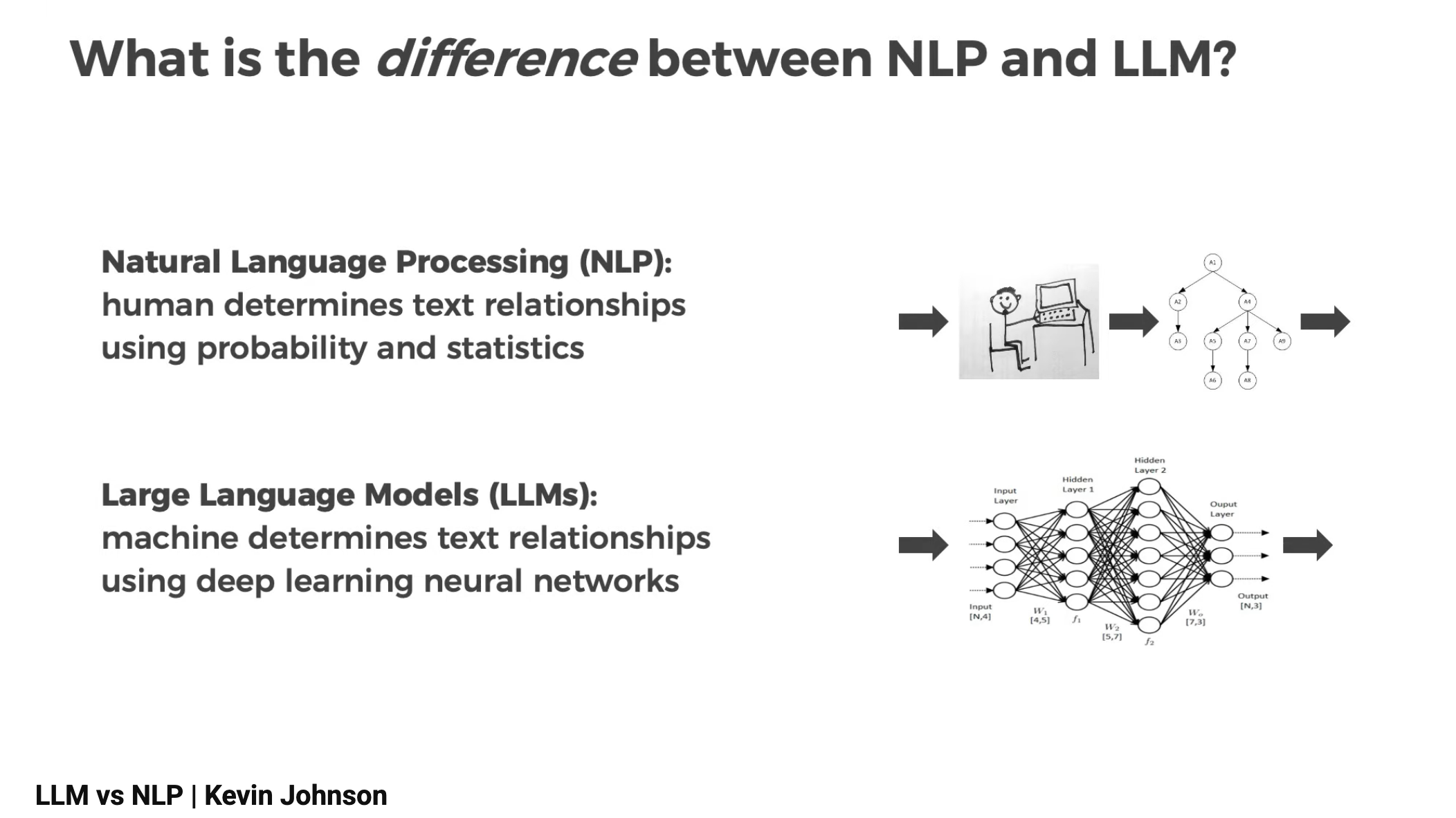
How NLP and LLMs Relate to Each Other
Despite their differences, both NLP and LLMs aim to solve the exact same fundamental problem:
Given a block of text, predict the next word.
In other words, NLP and LLMs do not understand and cannot think.
They calculate the probability of which word comes next.
Everything else, summaries, conversations, explanations, poems, emerges from this core ability.
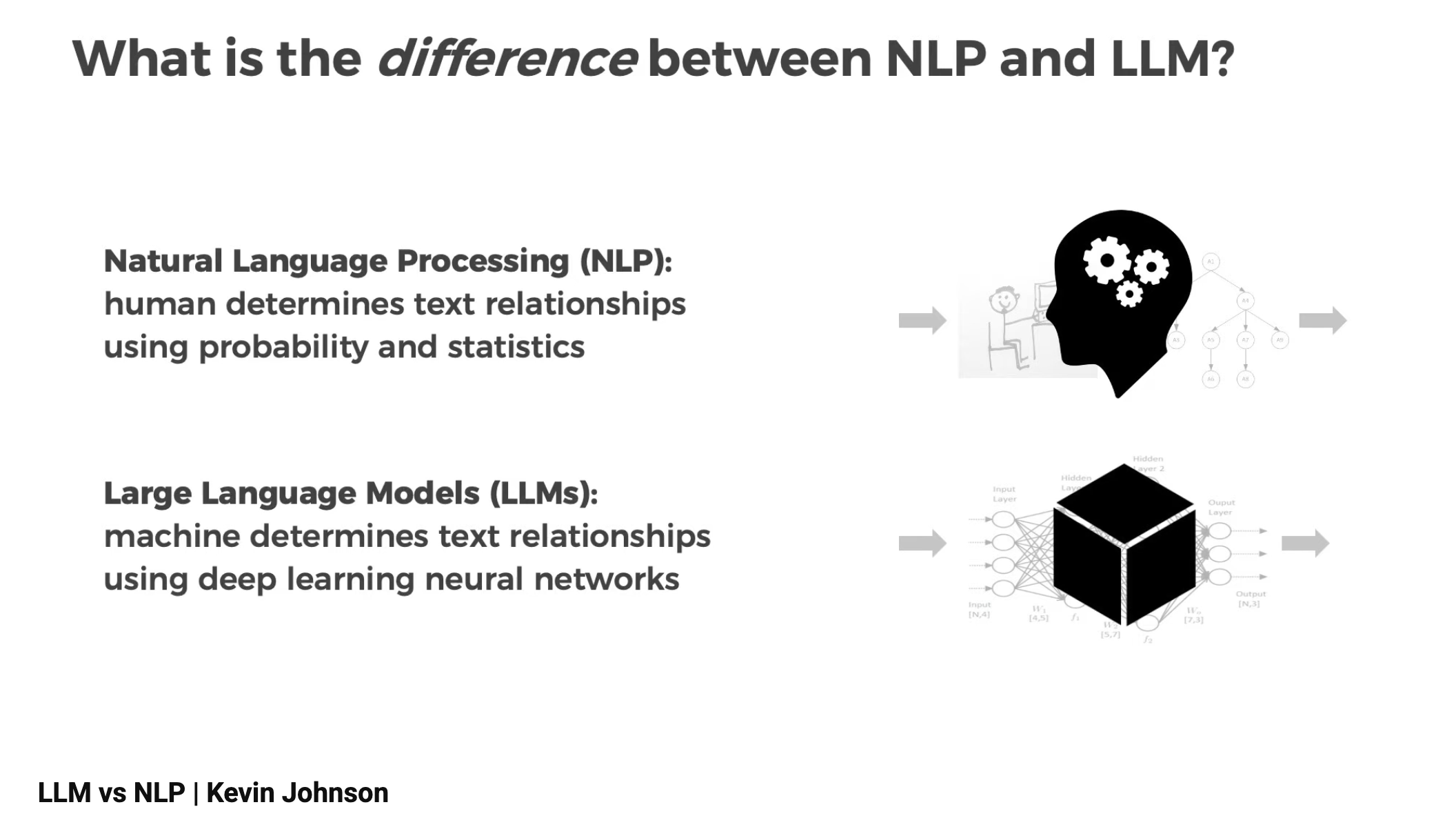
Think of NLP as the early phase of language technology and LLMs as the breakthrough that unlocked scale, context, and fluency.
- NLP = human-guided, statistical, predictable, narrow.
- LLMs = data-driven, deep learning–based, generative, and capable of handling long, complex tasks.
Overview of Different LLMs Used as AI Search Engines
When comparing large language models, it helps to understand what each was built for and where they shine. It's important to remember that they are just another AI marketing tool you can add to your stack.
Below is a clear, practical breakdown of Google Gemini, Anthropic Claude, Perplexity AI, and Microsoft Copilot all explained in a way that helps you select the right tool for content creation, automation, customer experience improvements, or workflow optimization.
According to Statista's research, ChatGPT is the most used solution for consumers, so that is a AI search tool everyone should get familiar with.
However, the companies building AI search engines are racing against one another and releasing better and better versions to beat the competition.
Google released a new Gemini 3 at the end of November 2025, and it has been widely praised even in the media as the best AI tool on the market.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is OpenAI’s conversational AI interface built on top of advanced large language models. While the underlying models handle the technical work, ChatGPT provides the user-friendly layer that makes those capabilities accessible through natural dialogue.
Typical Use Cases
- Content creation and refinement: Drafts blog posts, landing page copy, emails, scripts, and internal documentation. It can adapt tone, simplify language, or expand rough ideas into polished text.
- Summarization and analysis: Condenses long reports, transcripts, customer feedback, and research materials into clear outlines or key findings.
- Brainstorming and ideation: Produces campaign angles, messaging variations, naming options, and creative concepts to speed up planning and experimentation.
- Customer communication drafting: Generates first versions of support replies, onboarding sequences, and help center content to ensure consistent and clear messaging.
- Learning and explanation: Breaks down complex concepts, offers step-by-step reasoning, or simulates Q&A sessions for training, preparation, or onboarding.
- Technical assistance: Writes and explains code, generates documentation, or helps prototype small automations.
ChatGPT is widely used because it brings the power of generative AI into an intuitive conversational interface that fits naturally into everyday workflows.
Claude by Anthropic
Claude is known for its strong focus on constitutional AI, meaning it was built with safety, reasoning, and context retention at the forefront.
Typical Use Cases for Claude
- High-stakes content drafting: Policies, guidelines, customer communications, support scripts.
- Deep reasoning tasks: Strategy memos, step-by-step analysis, complex problem-solving.
- Long-context workflows: Reviewing long transcripts, reports, or legal-style documents.
- Creative ideation: Brainstorming campaigns, writing concepts, or generating narrative content.
Its clarity and structured output make it a strong fit for marketing, customer experience, and knowledge work where consistent tone and reliable reasoning matter.
Gemini by Google
Google’s Gemini family of models is designed to be deeply multimodal, meaning it can "understand" and generate text, images, audio, and video within a single architecture.
Typical Use Cases for Gemini
- Search and knowledge-heavy tasks: Summarizing documents, analyzing data, extracting insights.
- Multimodal workflows: Creating content that merges text with visual elements or interpreting screenshots and diagrams.
- Advanced productivity automation: Powering tools like Google Workspace for drafting emails, refining documents, or generating reports.
- Coding assistance: Offering structured code explanations, documentation rewriting, and debugging support.
Gemini is often suited for companies working with large information flows—ideal for improving documentation quality or generating well-structured content quickly.
Microsoft Copilot
Microsoft Copilot is an AI assistant built directly into Windows and the Microsoft 365 suite, including Outlook, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Teams, and more.
Instead of being a standalone chatbot, Copilot is embedded into everyday productivity tools, allowing users to combine generative AI with live documents, emails, data, and work-specific context.
Typical Use Cases for Copilot
- Document drafting and rewriting
Helps create or refine Word documents, proposals, internal memos, and reports using the surrounding context in your files. It can rewrite text, shorten content, expand sections, or adapt tone based on the document’s purpose. - Email assistance in Outlook
Drafts replies, summarizes long email threads, highlights action items, and helps prioritize communication. Useful for staying on top of high-volume inboxes. - Data analysis in Excel
Interprets datasets, builds formulas, identifies trends, summarizes complex spreadsheets, and generates charts. It can translate natural-language instructions directly into structured Excel outputs. - PowerPoint generation
Turns outlines, Word documents, or meeting notes into full slide decks with structured layouts and talking points. Great for speeding up internal and external presentation prep. - Meeting insights in Teams
Summarizes meetings in real time or after the fact, identifies decisions, generates follow-up tasks, and drafts shared recaps for the team. - Workflow and process automation
Supports task creation, document management, and cross-app actions throughout the Microsoft 365 environment, particularly valuable for enterprise teams with established workflows.
What Copilot Is Best For
Copilot is strongest when used inside the Microsoft ecosystem, where it can draw directly from your organization’s files, chats, emails, and meetings. It’s particularly effective for:
- Productivity enhancement across Microsoft 365
- Automating document, email, and data workflows
- Streamlining daily tasks for teams already using Office tools
- Enterprise environments with strict compliance and access control
- Creating polished documents and presentations using corporate context
Copilot’s key advantage is its deep integration: instead of switching tools or copying text into a chat window, users can activate AI directly where the work already happens.
Perplexity AI
Perplexity AI is a search-focused AI assistant designed to deliver fast, accurate answers grounded in verifiable sources. Unlike general-purpose chatbots, Perplexity combines large language model capabilities with real-time search, citation, and retrieval, making it a reliable tool for research-heavy tasks.
Typical Use Cases of Perplexity AI
- Real-time researched answers
Provides concise responses supported by citations, making it ideal for fact-checking, market research, and quick knowledge gathering. - Deep-dive exploration
Generates related questions, follow-up paths, and source overviews to help users explore topics more thoroughly. - Competitive analysis and industry insights
Summarizes reports, articles, and datasets using live information from trusted sources. - Technical and academic queries
Retrieves up-to-date information for scientific concepts, technical topics, or academic research where accuracy and sourcing matter. - Learning and onboarding
Helps users quickly learn new domains through structured, sourced explanations and topic overviews.
Perplexity AI is a strong fit for professionals who need fast, reliable answers backed by real-time information, ideal for research, analysis, and decision-making where accuracy and citations are essential.
| Model | What It Is | Typical Use Cases | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gemini (Google) | Multimodal large language model capable of processing text, images, audio, and video. | Research-heavy tasks, multimodal content creation, Workspace automation, coding assistance. | Multimodality, deep analysis, and strong integration with Google tools. |
| Claude (Anthropic) | Safety-driven model known for strong reasoning and extended context windows. | Long-form writing, policy creation, structured analytical work, summarizing long documents. | Clear reasoning, polished communication, and tasks requiring reliability. |
| ChatGPT (OpenAI) | Conversational interface built on OpenAI’s generative models. | Content creation, rewriting, summarization, brainstorming, customer communication drafting, explanations, coding. | Accessible general-purpose assistance and everyday conversational use. |
| Perplexity AI | Search-oriented AI assistant combining LLMs with real-time retrieval and citations. | Fact-checked answers, research summaries, competitive analysis, academic questions, rapid knowledge lookup. | Reliable, verifiable research backed by real-time information. |
| Microsoft Copilot | AI assistant embedded across Windows, Microsoft 365, and enterprise tools. | Email writing, Excel automation, meeting summaries, PowerPoint creation, workflow support, internal productivity tasks. | Productivity inside the Microsoft ecosystem, enterprise workflows, and automated document handling. |
Now that you understand what the different tools used as AI search engines are, let's move on to figuring out how to get your brand mentioned in them.
Traditional Keyword Search vs. AI Search in Plain Language
When people look for information, whether on a website, in a tool, or inside their own company, they generally type a question or a few words into a search box. How the system understands those words makes a huge difference.
Here’s the distinction in the simplest terms, using examples from the construction and renovation industry.
Traditional Keyword-Based Search
Traditional search works a bit like a filing cabinet. If the word you typed appears in a document, it shows it to you. If the word isn’t there, you probably won’t find what you’re looking for.
- It looks for exact matches of the words you type.
- If you type “roof leak repair,” on Google it only looks for websites with containing those exact words or variations of it
- It does not understand what you mean, only what you typed.
To get found by customers, you need to do search engine optimization.
Real-Life Example of Using Search Engines
Say you type: “fixing roof water damage”
If your website only mention “leaking shingles”, “roof moisture issues”, or “repairing roof underlayment,” traditional search may miss them completely, because the exact words weren’t a match.
It’s like asking a coworker about “water damage” and them replying, “I don’t know,” even though they have a whole manual labeled “moisture problems in roofing.”
Here's an example of searching in a traditional search engine. Note that it also features an AI-generated summary at the very top.
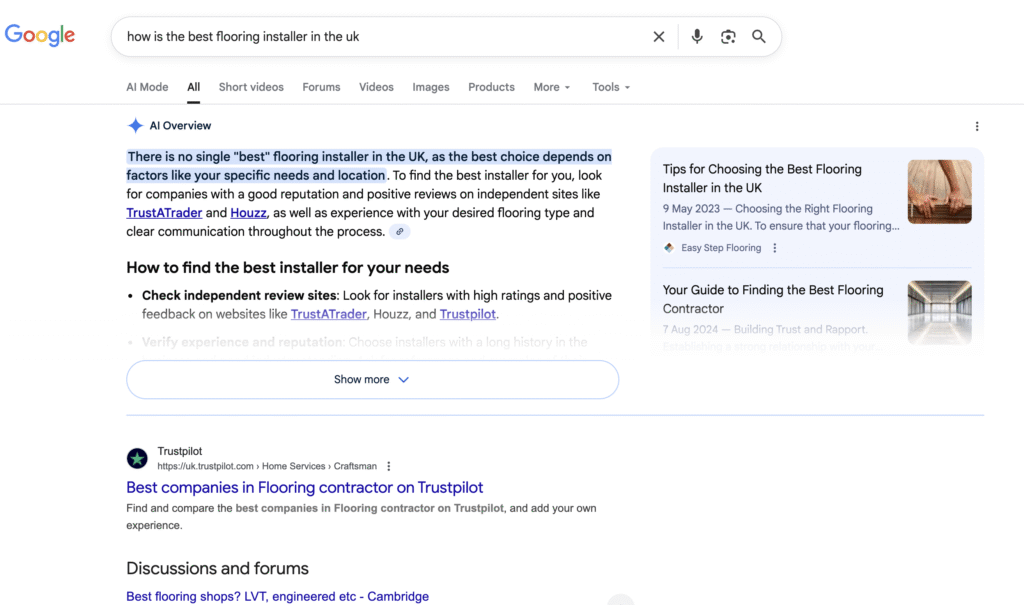
Strengths of Old-School Search Engines
- Simple and predictable, you get the same results every time.
- Works fine if you already know the exact term used.
Weaknesses
- If you don’t use the right wording, results won’t show up.
- Misses synonyms and alternative phrasing.
- Offers a long list of documents instead of giving a straight answer.
Traditional search is a good tool only when you know exactly what something is called.
AI Search
AI search works more like an experienced foreman who has seen everything and understands what you actually mean, even if you don’t say it perfectly.
This is unlike traditional search engines and their capabilities.
How AI Search Works
- It understands the meaning behind your words.
- Recognizes that “roof leak,” “shingle damage,” and “moisture under the roof deck” are connected.
- Reads and summarizes information automatically.
- Gives you direct answers instead of making you hunt through documents.
Example of AI Search in Construction
You type: “How do we prevent mold issues after a basement flood?”
AI search understands this includes topics like:
- Water damage restoration
- Drying timelines
- Ventilation
- Moisture meters
- Mold prevention steps
It may give an answer like:
“To prevent mold after a basement flood, ensure the area is dried within 48 hours, remove wet insulation, and run industrial dehumidifiers. Here are the exact guidelines from your moisture control manual.”
Even if your documents use completely different words, like “humidity mitigation”, AI search still connects the dots.

Strengths
- Understands natural language questions (“How do I…?”)
- Finds relevant info even without exact wording
- Provides a straight answer instead of 20 links
- Handles complex problems easily
- Speeds up training for new workers who don’t know the precise terms yet
Weaknesses
- Not always 100% predictable
- Needs more computing power
- Requires guardrails to avoid mistakes
- Ai generated summaries and searches can hallucinate and produce misleading information
Does AI Search Matter for Home Improvement and Construction Companies?
The construction and home-improvement field is full of moving parts, specialized terminology, local slang, and several different ways to describe the very same issue.
A single structural problem might be talked about as a settling foundation, a cracked slab, uneven floors, or a structural shift. Traditional search engines often treat these phrases as unrelated queries.
AI search doesn’t.
Modern AI-powered search engines understand intent and context rather than relying on exact keyword matches. Instead of treating each variation as a separate problem, they recognize the concepts behind the words and connect them. This makes it far easier for homeowners, subcontractors, office staff, and field crews to find the right information, fast.
This matters even more in construction environments where:
- Terminology varies across regions and trades
- Customers rarely use “technical terms” when describing issues
- Few tradespeople have experience in building websites and online visibility
The opportunity for construction companies becomes even bigger when you consider how AI evaluates businesses online.
AI systems increasingly rely on signals like customer reviews, structured data, and high-quality service descriptions to determine which businesses to recommend.
When your company consistently uses clear language online, publishes project examples, and displays verified reviews in formats AI can read, you’re far more likely to appear in these AI-driven search results.
Get inspired by recent articles:
- Digital marketing for electricians
- Digital Marketing for Solar Companies: How to Attract More Customers and Build Trust
- Local Marketing for Plumbers: Without Any Buzzwords
- 3 Digital marketing tips for small businesses
How to Get AI Search to Recommend Your Business (Using Customer Reviews)
- Make your reviews “AI-readable.” Use structured data, e.g. the Review and AggregateRating schema, so that AI tools and search engines can parse your reviews, star ratings and overall reputation as machine-readable facts.
- Host reviews on an authoritative page. Having a dedicated, third-party–hosted review page (for example on Trustmary) gives AI tools a stable, credible source they can trust and reference.
- Keep fresh, relevant reviews flowing. Recent positive reviews strengthen your credibility, AI search increasingly favors businesses with consistent, up-to-date feedback rather than a few old testimonials.
- Showcase detailed, quotable reviews. Reviews that clearly describe services, results, and customer satisfaction give AI more context to understand what you offer and how well you deliver.
- Ensure broad visibility across the web. Reviews on multiple platforms (website, review sites, directories, social media) help AI cross-validate your reputation — making recommendations based on a richer trail of evidence.
Now that you know what AI search is, dive into how to optimize for AI searches. And start collecting reviews to be reliable in the eyes of potential customers and AI bots.
FAQ: AI Search and How It Affects Businesses
What is AI search, and how is it different from traditional search engines?
AI search doesn’t rely on matching exact keywords. Instead, it understands the meaning behind queries, connects related terms, and evaluates broader context. This helps people find accurate answers even if they use slang, vague wording, or multiple ways to describe the same issue.
AI search, in a way, does the heavy lifting of sifting through search results, and provides users with a best guess of what they need.
Why does AI search matter for local service businesses like construction or renovation companies?
Because customers rarely know the correct terminology and search using symptoms, guesses, or everyday language. AI search is designed to interpret those natural phrases and still surface the right services. Businesses that present clear, trustworthy information online benefit the most.
How do customer reviews influence AI-driven recommendations?
AI models use reviews as a trust signal. They look at recency, detail, sentiment, and whether reviews can be read as structured data. When your reviews are consistent, machine-readable, and spread across reliable platforms, AI is more likely to recommend your business.
What type of content helps AI search understand what my company actually does?
Structured service descriptions, detailed project examples, FAQs, and clear language that reflects how customers talk about problems. When combined with verifiable third-party reviews, this creates a strong evidence base AI systems can rely on.
How can my company prepare for the shift toward AI-generated search results?
Make your reviews machine-readable, keep them fresh, describe your services in plain language, and ensure your reputation is visible on trusted pages. These steps help AI interpret your business accurately and increase your chances of being highlighted in AI-powered answers.